
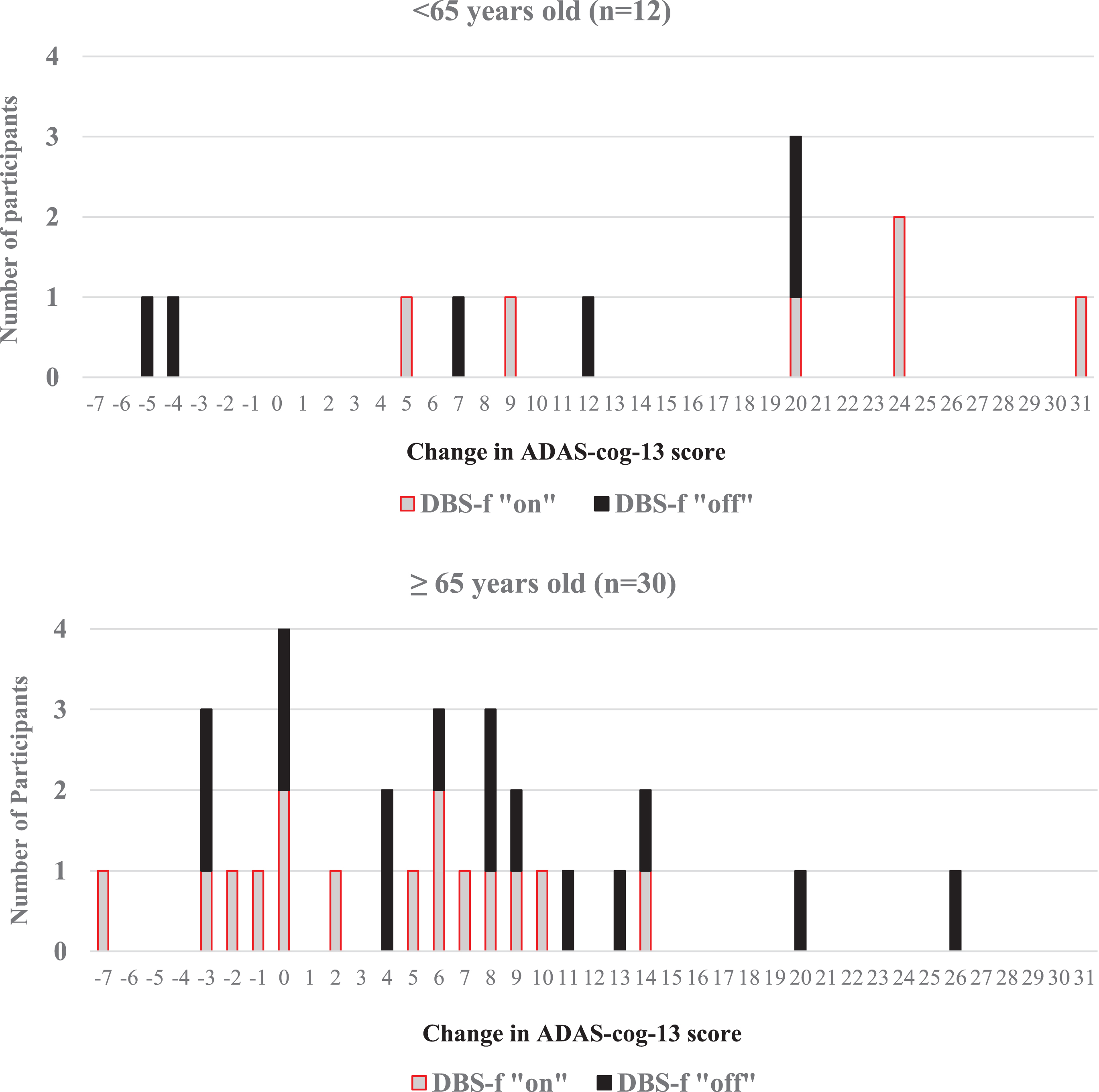
Our data also suggest that age, gender, age at onset of dementia, level of education, and use of estrogen (in women) or anti-inflammatory drugs are related to cognitive abilities in AD. Ada is an unincorporated community in Ottawa County, Kansas, United States. 2 ADAS-Cog is the most common cognitive assessment instrument used in AD clinical trials all over the world. Because age, MMSE score, and GDS stage (and not the ADAS-Cog) are commonly used to select subjects for AD clinical trials, our data should improve the ability of sponsors to predict ADAS-Cog scores of the subjects in their trials on the basis of the inclusion criteria used. / 39.15139°N 97.88917°W / 39.15139 -97.88917. We also present data on the distribution of ADAS-Cog scores in relation to subjects' age, level of education, MMSE score, and GDS stage. Background: The Alzheimers Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive (ADAS-Cog) has been used widely as a cognitive end point in Alzheimers Disease (AD) clinical. In a multiple regression model, younger age, male gender, older age at onset of dementia, use of concurrent estrogen, and use of concurrent anti-inflammatory agents were statistically significantly associated with superior cognitive performance. Correlations among the ADAS-Cog items ranged from 0.19 to 0.59 and all were statistically significant (p < 0.0001). The ADAS-Cog score was statistically significantly correlated with MMSE (R = -0.76, p < 0.0001) and GERRI (R = 0.40, p < 0.0001) total scores. At baseline, the mean (+/-SD) MMSE score was 18 +/- 4, the ADAS-Cog score was 28 +/- 11, and most subjects were in GDS stage 4 or 5. We used data from 1,648 AD participants in two identical 26-week multicenter drug trials to examine the distribution of baseline ADAS-Cog scores in relation to selected demographic and clinical variables, Mini-Mental State Exam (MMSE), Global Deterioration Scale (GDS), and Geriatric Evaluation by Relative's Rating Instrument (GERRI) scores. The cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-Cog) is used as an efficacy measure in clinical drug trials of Alzheimer's disease (AD).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
